The Essential Guide to End-to-End Software Testing
Introduction
When it comes to delivering a flawless user experience in the digital realm, thorough software testing is the linchpin that holds everything together. Among the various testing methodologies, End-to-End Testing stands out as a comprehensive approach that ensures all components of an application work seamlessly together.
End-to-end (E2E) testing is a software testing methodology that verifies the working order of a software product in a start-to-finish process. End-to-end testing verifies that all components of a system can run under real-world scenarios.
The goal of this form of testing is to simulate a user experience from start to finish. E2E testing can find software dependencies while also validating the system under test, its data integrity and integrations.
Some of the key characteristics of E2E testing:
Focuses on user experience: It prioritizes testing from the user's perspective, ensuring the application behaves as expected throughout their journey.
Covers all components: It encompasses the entire application workflow, including front-end interfaces, back-end processes, databases, and external integrations.
Emphasizes data flow: It tracks data as it moves through the system, verifying its accuracy and integrity at every step.
Often automated: While manual testing is possible, E2E testing is often automated using specialized tools to improve efficiency and repeatability.
Why Understanding User Goals Matters in E2E Testing
At the heart of successful end-to-end testing lies a clear understanding of what real users are trying to achieve. Users don’t log onto an application just to marvel at its bells and whistles—they’re there to accomplish a task or solve a problem. By centering testing efforts around genuine user goals, development teams ensure the application delivers practical value, not just feature checklists.
This user-centric approach means:
Tests mirror real-world usage: Crafting test scenarios based on actual user workflows (like purchasing a book on Amazon or checking in for a flight on Expedia) leads to uncovering issues that strictly technical tests might miss.
Greater business impact: When testing validates that users can seamlessly achieve their objectives—be it ordering a pizza or scheduling a video call—the application is far more likely to drive user satisfaction and loyalty.
Holistic coverage: Focusing on user goals naturally pulls in all parts of the system, from UI design quirks to underlying database flows, and even third-party integrations.
While gathering detailed user insights can require extra effort—surveys, interviews, or involving “beta testers”—incorporating these perspectives is what transforms an ordinary system check into truly rigorous quality assurance. Skipping this step can mean missing the mark on what actually matters to the people who use the product daily.
End-to-end (E2E) testing is most effective when it is integrated into the development process, providing a strong validation mechanism at key points. Let’s illustrate this with an example. Imagine a scenario where a user wants to watch a movie on an OTT (Over-The-Top) app. Typically, such an application would follow a flow where each step is dependent on the successful execution of the previous one.
Login: The test starts with a user logging into the OTT app using valid credentials. This step ensures that the login functionality is working correctly.
Browse Content: The user explores the library by browsing categories, searching for specific titles, or using the “Continue Watching” section. This verifies smooth navigation, effective search functionality, and content loading.
Movie Selection: The user selects a movie to watch. This step checks that the movie details, such as synopsis, cast information, and trailers, load accurately.
Playback: The user begins watching the movie, testing the video playback functionality. This includes smooth streaming, subtitle availability, and the ability to adjust playback settings.
Continue Watching: After watching for a while, the user pauses playback and exits the app. The test ensures that the app remembers the user's progress, and the movie appears in the “Continue Watching” section upon reopening the app.
This is a basic flow that covers essential functionalities an OTT application should provide. Additional functionalities can be included for broader test coverage, such as downloading content, multi-profile support, parental controls, handling network connectivity issues, and managing content missing errors.
By conducting these E2E test scenarios, the OTT platform can ensure it delivers a robust, bug-free application to end-users. This type of testing should be performed once all individual features have been tested and integrated. In the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC), E2E testing is done after the development phase of an iteration is complete and before the software is released to end-users. This acts as a checkpoint, ensuring confidence in the product's reliability and performance.
The Necessity of Automated End-to-End Testing as Your Project Scales
As applications grow larger and more complex, manual end-to-end (E2E) testing quickly becomes impractical. Imagine trying to keep track of every possible user journey on an expanding platform—clicking through each path, testing every feature, and repeating these steps after every update. It’s like trying to find a specific scene in a library of movies, one DVD at a time.
That’s where automation steps in to save the day. Automated E2E testing tools—such as Selenium, Cypress, and Playwright—allow you to script user interactions and run them automatically. This means you can routinely test entire workflows, including login, purchases, and more, without lifting a finger each time. With automation:
Tests can run continuously as new code is introduced, ensuring fresh features don’t accidentally break existing ones.
Regression testing becomes effortless, freeing up your team’s time for more exploratory or creative testing tasks.
Bugs are spotted earlier in the development cycle, which saves time, reduces frustration, and keeps release schedules on track.
In short, automation isn’t just a luxury as your project grows—it’s a necessity for maintaining quality, speed, and peace of mind in an ever-changing codebase.
The Importance of User Goals in E2E Testing
A crucial aspect that often sets successful end-to-end testing apart is a deep understanding of user goals. Ultimately, users aren’t interacting with your application for the sake of fancy features—they’re on a mission to achieve something specific, whether it’s catching up on the latest binge-worthy series or finding that elusive cult classic. When E2E tests are designed with genuine user intentions in mind, they provide far more value than simply ticking off feature checkboxes.
That means E2E testing should go beyond verifying technical requirements. It’s about validating that the full workflow actually enables a user to reach their intended outcome without frustration or unexpected roadblocks. For example, if a key objective for an OTT app user is to seamlessly resume a series across devices, robust E2E tests will simulate and confirm that experience end-to-end—not just that data sync occurs somewhere behind the scenes.
However, accurately capturing these user goals can be a challenge. Not every development team has a crystal-clear picture of every user intention from day one. Investing in user research or gathering feedback from early adopters (think: beta testers) can help bridge this gap, but it does take time and resources. Still, prioritizing user-focused scenarios pays dividends—helping uncover usability issues, edge cases, or workflow gaps that purely technical tests may miss.
In the competitive landscape of software today, crafting E2E tests around what truly matters to users is not just smart QA practice—it’s a strategic move to deliver products that delight, not disappoint.
How E2E Testing Differs from Other Testing Methods
While end-to-end (E2E) testing provides a holistic examination of an application’s complete workflows, it’s just one piece of the quality assurance puzzle. E2E testing works best in tandem with other testing approaches, each serving a distinct purpose within the software development process.
Unit Testing: This form of testing zeroes in on individual components or functions, validating that each piece works as designed in isolation. Think of it as checking each brick in a wall before assembling the structure.
Integration Testing: Here, the focus is on the interaction between modules or services. It verifies that distinct features or components play nicely together once combined, catching any incompatibilities early.
Security Testing: This ensures the application stands strong against external threats by identifying vulnerabilities and safeguarding sensitive data.
Accessibility Testing: To create truly inclusive digital experiences, accessibility testing confirms that the software can be used effectively by people with various disabilities. It adheres to standards like WCAG and Section 508, ensuring features work seamlessly with assistive technologies.
Usability Testing: This evaluates how intuitive and user-friendly the application is. By observing real user interactions, usability testing highlights obstacles in navigation, functionality, or design that could hinder a smooth experience.
Unlike E2E testing, which simulates full workflows from start to finish, these methods target specific layers of the application. A robust quality strategy combines all of these, layering their strengths to deliver a secure, reliable, and accessible product.
How E2E Testing Differs from Other Testing Methods
While end-to-end (E2E) testing provides a holistic view of the user journey, it’s only one piece of the broader testing puzzle. In a typical software development process, E2E tests are complemented by several other testing types, each serving a specific purpose:
Unit Testing: This digs right down to the roots, verifying the smallest components of an application—think of individual functions or classes, tested in isolation. The goal here is to catch bugs early at the source.
Integration Testing: After building the building blocks, integration testing checks whether those blocks play nicely together. It validates the interaction between combined modules, catching issues that might only surface when different parts of the application meet.
Security Testing: Here, the focus shifts to defending the software’s integrity. Security testing identifies vulnerabilities, helping to safeguard sensitive data and protect against unauthorized access and external threats.
Accessibility Testing: Not every user interacts with an application the same way. Accessibility testing ensures the product is functional for people of all abilities—covering everything from screen reader compatibility to keyboard navigation, and conforming to established standards like WCAG.
Usability Testing: Finally, usability testing takes the application for a spin from the user's perspective, assessing how intuitive and straightforward it is to complete tasks. The aim is to make the experience smooth and frustration-free.
In contrast to these more targeted approaches, E2E testing is all about validating how these pieces come together in real-world scenarios—from the login screen to complex workflows. Effective testing strategies weave E2E tests together with these other layers, creating a safety net that ensures quality at every level of the application.
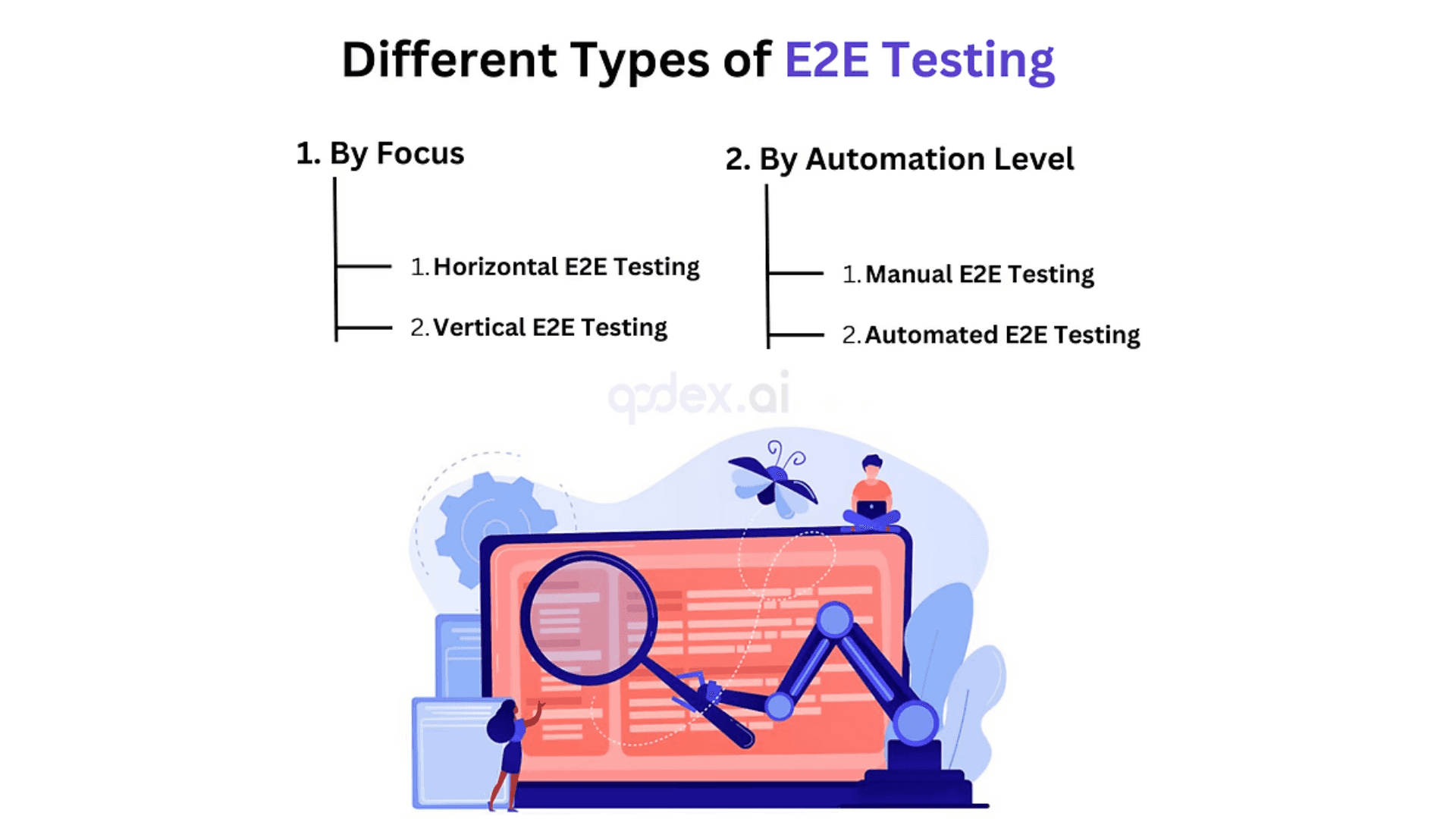
Different Types of End to End Testing
There are two primary ways to categorise E2E testing approaches:
By Focus and By Automation level
By Focus:
Horizontal E2E Testing: This approach examines a broad user journey across multiple functionalities. It’s like testing the entire checkout process on an e-commerce site, from browsing products to placing an order and receiving confirmation.
Vertical E2E Testing: This method delves deeper into a specific feature or functionality, ensuring all its underlying components work seamlessly together. For instance, on the same e-commerce site, vertical E2E testing might focus solely on the shopping cart functionality, checking if items can be added, removed, and if quantities can be adjusted correctly.
By Automation Level:
Manual E2E Testing: This traditional approach involves a human tester manually navigating through the application, simulating user journeys, and noting any issues. While it can be time-consuming, manual testing is valuable for exploratory testing or tasks that require human judgment.
Automated E2E Testing: This method uses automation tools and frameworks to script user actions and automate test execution. It enables faster and more repetitive testing, making it ideal for regression testing or ensuring core functionalities remain intact after code changes.
Why Can E2E Testing Be Time-Consuming?
End-to-end testing often demands significant time and effort, and here’s why. Crafting comprehensive E2E test cases requires a deep understanding of your application’s business logic and the various user journeys within it. Since these tests mimic real user interactions from start to finish, setting them up involves coordinating across different components, dependencies, and sometimes even external systems—think payment gateways, email services, or third-party APIs.
Additionally, because E2E tests replicate full workflows (from login to checkout or from content browsing to video playback), they tend to run slower than simpler unit or integration tests. Each test may need to spin up a realistic test environment, populate databases, and interact with the application’s interface—much like a user would. Running these tests on staging environments instead of live production helps catch potential issues without disrupting users, but it also means tests are frequently reserved for critical flows and executed less frequently to balance thoroughness with development speed.
All of this makes E2E testing a valuable yet resource-intensive checkpoint in your quality assurance process, ensuring user experiences remain seamless even if it requires a little more patience up front.
When Should You Automate End-to-End Testing?
Manual end-to-end testing has its place, especially for ad hoc scenarios or when exploring new features. However, as your application scales and the number of user journeys grows, relying solely on manual methods quickly becomes impractical. Imagine having to test every possible interaction in a large e-commerce site by hand—it’s like searching for a needle in a haystack every time you make a tiny update.
Automation steps in as your testing lifeline in a few key situations:
Frequent Releases: If your team is shipping features or updates regularly—think weekly sprints or continuous deployment—automation ensures consistent test coverage without slowing you down.
Complex User Flows: When your application’s workflows expand, encompassing multiple integrations or dependencies, automating those end-to-end scenarios helps maintain reliability while reducing human error.
Regression Testing: Each time your codebase changes, automated E2E tests can quickly validate that critical user paths still function as intended, saving hours (or even days) of manual labor.
Repetitive Tasks: Tests that run often and need to cover the same steps across various browsers, devices, or data sets are prime candidates for automation using tools like Selenium, Cypress, or Playwright.
In essence, once your project reaches a certain size, automating E2E tests isn’t just convenient—it’s essential for timely, thorough, and repeatable testing. This not only speeds up your development cycles but also builds confidence that your application works as intended, release after release.
Why Is End-to-End Testing So Time-Consuming?
End-to-end testing often requires a significant investment of time for several reasons. First, crafting comprehensive test cases isn’t just about ticking checkboxes—it’s about truly understanding how users move through your application. Each scenario must mirror real-world workflows, making the planning and design process far more intricate than with isolated unit or integration tests.
Another factor is the complexity of simulating real user interactions across all the moving parts of your system. These tests often mimic full user journeys, touching everything from backend APIs to frontend interfaces, and even third-party integrations like payment gateways or external data providers. As a result, they can take considerable time to execute, especially compared to the lightning speed of unit tests.
Because of their scope and intensity, end-to-end tests are typically reserved for your most mission-critical flows—for example, a Stripe-powered checkout or a user sign-in with Google OAuth. Since these scenarios require a pristine, production-like environment to catch subtle bugs, they’re usually run in staging rather than during every step of development. This balance ensures your testing process is thorough, without slowing down the pace of daily builds or releases.
How to Perform End to End Testing?
End-to-end (E2E) testing goes beyond individual components testing in software development, ensuring a seamless user experience from start to finish.
Test Planning
Before writing your test cases, outline the scope for end-to-end testing. Identify the key features and functionalities that need testing, as well as the user journeys and interactions to validate. Consider any risks and dependencies that could affect your testing process. Clearly defining your test scope will help you concentrate on the most critical aspects of your system while avoiding unnecessary scenarios.
Set up a dedicated testing environment that mirrors the production setup as closely as possible. This ensures that tests accurately reflect real-world conditions.
Choose end-to-end testing tools like Selenium, Cypress, Appium, or Qodex.ai, depending on your application’s technology stack and specific requirements.
Designing and Developing Test Cases
Once your scope is defined, the next step is to design and develop your test cases, using user requirements and specifications as your guide. A well-crafted test case should have a clear and descriptive title, a list of preconditions and assumptions, a sequence of steps to follow, and an expected outcome. Additionally, include any necessary data, parameters, or variables.
The key to a well-designed test case is that it should be easy to understand, execute, and update.
Prioritise core functionalities and high-impact user journeys first to ensure critical areas are thoroughly tested within time constraints. Utilizing a tool like Qodex.ai for end-to-end testing can streamline this process, ensuring comprehensive and efficient testing of your application.
Test Analysis and Execution:
Execute your test cases manually or use automation tools for efficiency. Automating test cases can save time and effort, while enhancing the reliability and consistency of your end-to-end testing.Develop a strategy for when and how to execute your test cases. They can be run before or after each deployment, on a scheduled basis, or on demand. It's also essential to monitor your test cases effectively. Utilize dashboards, reports, or alerts to track progress. Regularly running and monitoring your test cases ensures your system functions correctly and allows you to promptly address any issues or bugs.
Continuous Improvement:
Regularly update and enhance your test cases as the application develops to incorporate changes and new features. Integrate E2E tests into your Continuous Integration and Delivery (CI/CD) pipeline. This enables automated testing with each code commit or build, allowing you to catch issues early on. . Many teams integrate these tools into their CI/CD pipelines to automate the execution of E2E tests. This automation ensures that tests are run consistently and reliably as part of the deployment process, helping to identify issues early and improve software quality continuously. Continuously analyze test results and adjust your E2E testing strategy to better meet user needs.
By adhering to these best practices and continually refining your approach, you can perform effective end-to-end testing to ensure your software delivers a seamless and user-friendly experience. Keep in mind that end-to-end testing is an ongoing process, not a one-time task. It evolves with your software, consistently maintaining its quality and enhancing user satisfaction.
Challenges in Designing End-to-End Tests
Designing effective end-to-end (E2E) tests often presents its own unique hurdles. Since these tests seek to mimic how real users interact with your application, you must account for a multitude of possible user journeys and device environments. For example, a single workflow—like logging in and streaming a movie—might need to work flawlessly across Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge, each with their quirks and rendering differences. This multiplies the scenarios that must be covered and increases the intricacy of test maintenance.
Additionally, E2E tests typically involve coordinating several system components at once—APIs, databases, user interfaces, third-party integrations, and more. Ensuring that all these pieces communicate smoothly, especially as your application evolves, can quickly become a time-consuming jigsaw puzzle.
Another layer of complexity emerges when managing test data and preparing the system state before executing tests. Unlike more isolated or “unit-level” testing, E2E scenarios often require the app data to be in a particular condition—say, a user with an active subscription, or a video half-watched. Setting up and tearing down this data in a repeatable way isn’t always straightforward.
All these moving parts mean more opportunities for flaky tests, where factors outside your code—like network speed, browser updates, or third-party service outages—can cause inconsistent results. This not only slows feedback for your development team but can chip away at confidence in your automation suite, if not managed carefully.
E2E testing is essential for gaining a full picture of your user experience, but designing comprehensive, stable tests demands strategic planning and ongoing commitment.
Main Challenges of End-to-End Testing
While end-to-end testing is crucial for delivering a reliable and seamless software experience, it’s not without its hurdles. Understanding and addressing these challenges can help your team implement a more effective testing strategy.
1. Time and Resource Intensive
Designing, developing, and maintaining E2E tests often requires a significant investment of time and resources. Unlike unit tests, these tests must simulate realistic user journeys across multiple systems and interfaces, which means writing and executing them can be slow and computationally demanding. Teams often prioritize E2E tests for the most essential user flows to avoid bogging down development cycles with long test runs, especially in staging or pre-production environments.
2. Complexity in Test Design
Simulating genuine end-user behavior across diverse platforms, devices, and browsers poses design challenges. For instance, ensuring your web application works seamlessly on Chrome, Firefox, and Safari may call for tailored test cases for each environment, increasing maintenance overhead. Capturing all possible user interactions, edge cases, and integration points amplifies this complexity even further.
3. Understanding True User Needs
E2E testing is most impactful when it focuses on how well the software helps users accomplish their goals. However, development teams don’t always have a crystal-clear view of real-world user expectations. Gathering authentic user insights often involves detailed research or the recruitment of beta users—both of which can stretch timelines and budgets. Without this perspective, tests may validate features rather than meaningful outcomes.
Despite these challenges, end-to-end testing remains one of the most valuable tools for validating software in real-world scenarios. When approached thoughtfully, it helps ensure that your application not only meets technical standards but also delivers real value to users.
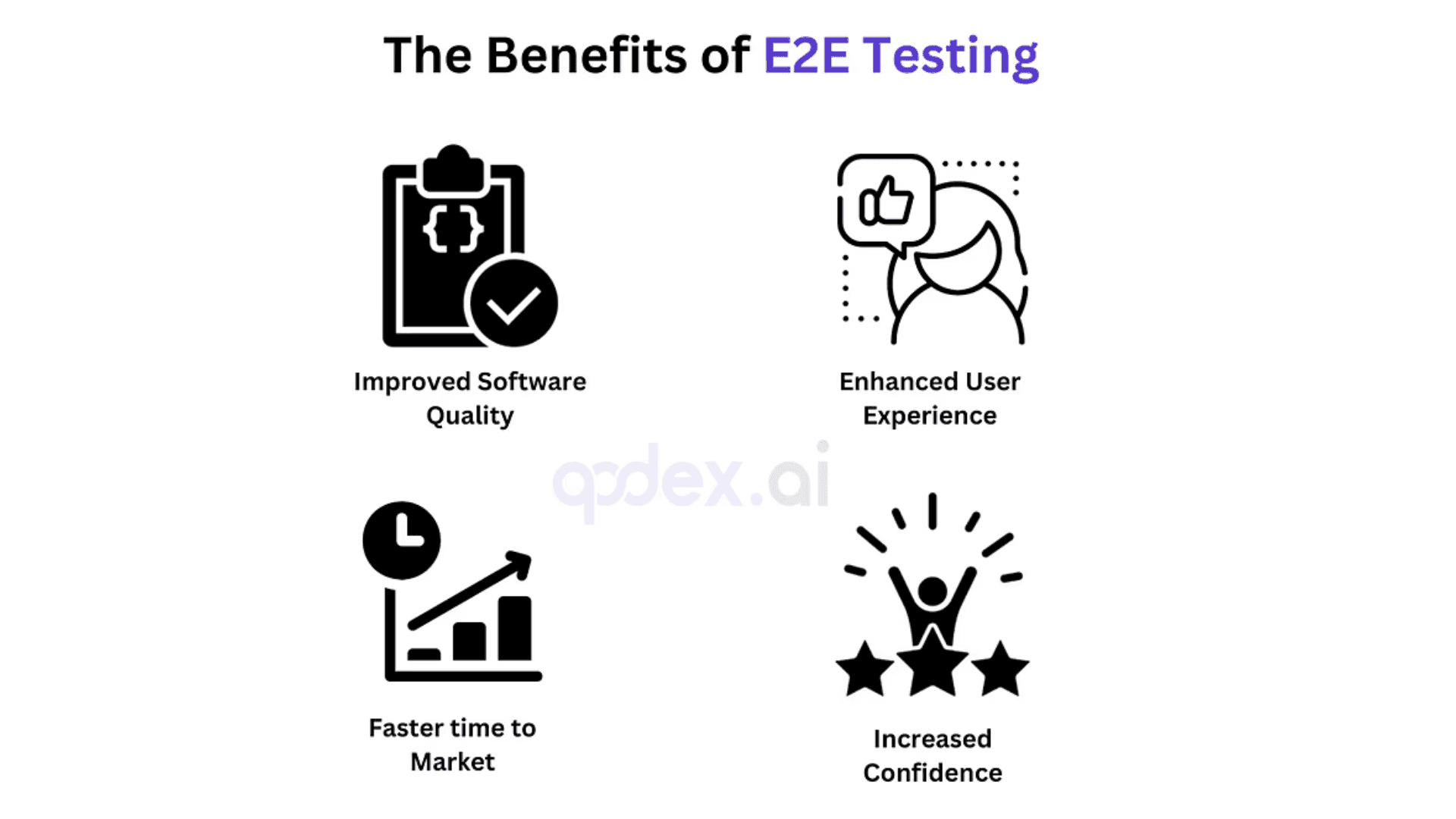
Benefits of E2E Testing:
Improved software quality: Catches complex bugs and integration issues that might be missed with unit or functional testing.
Enhanced user experience: Ensures a smooth and consistent user journey, boosting user satisfaction and retention.
Faster time to market: Detects problems early on in the development process, preventing costly delays in deployment.
Increased confidence: Provides evidence that the application functions correctly under real-world conditions.
Challenges in Designing E2E Tests
Designing end-to-end (E2E) tests can be surprisingly complex, primarily because these tests must capture the full scope of real user interactions with your application. Unlike unit tests or integration tests, E2E tests don’t just check one feature—they replicate complete workflows, which means every system component gets involved.
Here’s why it’s tricky:
Multiple Environments: Users may access your application from different browsers (Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge), operating systems, and devices. Each platform may behave slightly differently—and that means test cases need to cover all these combinations to catch platform-specific issues.
Evolving Features: As software evolves, features change, and new user scenarios emerge. Your E2E test suite must keep pace, expanding to cover updated flows while ensuring nothing critical gets missed. This constant upkeep can quickly balloon the scope of your testing effort.
Numerous Dependencies: E2E tests often rely on several integrated services—databases, third-party APIs, authentication systems, and more. Any changes or outages in these dependencies can complicate test reliability, making the suite harder to maintain.
Resource Intensive: Simulating real-world scenarios in full can require substantial setup, including mock data, dedicated test users, and orchestrating multiple systems. As a result, E2E tests tend to be slower and more resource-intensive than simpler types of tests.
Ultimately, the broad scope and the need to account for real-world variability mean E2E test design is both essential and challenging. Thorough planning makes all the difference.
Advantages for Developers and QA Teams
End-to-end testing isn't just about spotting user-facing bugs—it also streamlines workflows for both developers and QA teams. With well-structured E2E testing practices, organizations can allow dedicated QA professionals to focus on building comprehensive, user-centric test scenarios, freeing up valuable developer time. This lets developers channel their energy into building new features and refining the application's architecture rather than being bogged down by manual testing cycles.
Modern E2E testing tools like Selenium, Cypress, and Appium integrate seamlessly into automated CI/CD pipelines. This means that whenever code changes are pushed, E2E tests can be triggered automatically. Developers receive immediate feedback on potential issues, catching integration or regression bugs before they reach production. For QA teams, this automation supports rapid test execution and consistent coverage—no step is skipped, and no critical flow goes untested.
In a collaborative DevOps environment, this synergy leads to:
Faster feedback loops: Developers and testers can detect and resolve issues earlier.
Reduced manual testing effort: QA teams automate repetitive test cases, focusing on exploratory testing or complex scenarios.
Improved release confidence: Automated E2E tests validate that new code works well with existing features, ensuring each deployment is stable.
Streamlined handoffs: Clear test results and actionable reports simplify communication between development and QA.
Ultimately, this shared responsibility enhances both productivity and product quality.
How E2E Testing Empowers Managers
For managers steering a software project, end-to-end testing offers much more than just catching bugs—it delivers actionable insights into how the entire application functions as a cohesive whole. By simulating real-world scenarios and user flows, managers can pinpoint which areas of the system have the greatest impact on the user experience and business goals.
This bird’s-eye view allows for smarter prioritization of development efforts. With comprehensive E2E test results in hand, managers can:
Focus teams on the features or workflows most critical to end users
Quickly identify bottlenecks or risky integration points
Allocate resources efficiently by addressing high-impact issues first
Ultimately, this leads to better decision-making, optimized use of team capacity, and greater alignment between technical improvements and overall business objectives. E2E testing transforms complex system data into clear, actionable priorities—resulting in a more stable product and greater customer satisfaction.
Benefits for Developers and QA Teams
End-to-end testing isn’t just a win for end users—it’s equally advantageous for development and QA teams themselves. For developers, it means less time wading through bug reports after release, and more time focused on crafting new features and improving your application. With a robust E2E process in place, many potential headaches are caught early, which translates to smoother sprints and fewer last-minute fire drills.
QA teams reap the rewards as well. Since E2E testing is designed with user workflows in mind, test cases reflect actual user behavior—which makes them both relevant and pragmatic. This allows QA specialists to spot usability issues that would otherwise slip through the cracks. Plus, using automation tools like Selenium, Cypress, or Appium, testers can integrate these checks directly into CI/CD pipelines. Updates are thoroughly vetted with every commit, providing immediate feedback; if something breaks, fixes can be made before they snowball into bigger problems.
Ultimately, end-to-end testing promotes a collaborative environment, where everyone can trust that changes are safe, stable, and user-friendly—whether you’re writing the code or ensuring its quality.
Why E2E Testing Matters for Managers
For managers, end-to-end testing offers much more than technical assurance—it delivers strategic oversight. By simulating real user interactions across the full application, E2E testing makes it easier to spot and resolve high-impact issues before they reach production. This visibility empowers managers to:
Allocate resources more efficiently, focusing teams on the most business-critical workflows.
Set clearer priorities based on actual system behavior and user journeys, reducing guesswork.
Communicate testing progress and application health confidently to stakeholders, thanks to comprehensive test reporting from platforms like Selenium and Cypress.
Build trust within the team and with leadership, knowing that the application is robust, reliable, and ready for users.
Ultimately, robust E2E testing practices give managers the data and confidence needed to steer development efforts toward higher quality and user satisfaction—while minimizing the risk of costly late-stage surprises.
Enhancing Software Quality
By detecting and addressing potential issues early in the development cycle, End-to-End Testing helps improve the overall quality of the software application. This proactive approach not only ensures a more stable and reliable product but also helps reduce the time and effort required for bug fixing later in the development process. Ultimately, End-to-End Testing contributes to delivering a high-quality product that meets the expectations of users and stakeholders alike.
Transitioning from Manual to Automated E2E Testing
As your application scales and the number of user journeys increases, transitioning from manual to automated end-to-end (E2E) testing becomes crucial for maintaining efficiency and test coverage. Making this shift requires careful planning and adherence to best practices for a smooth, successful implementation.
Best Practices for Moving to Automation:
Identify High-Impact Scenarios: Start by selecting user flows that are critical to your application's functionality and user experience. Automate the tests that deliver the most value and are performed frequently.
Choose the Right Tools: Opt for automation frameworks that align with your team’s skill set and your application's technology stack. Popular options include Cypress, Puppeteer, and Katalon Studio—all offering robust support for E2E automation.
Modularize Test Scripts: Break your tests into reusable modules or components. This makes maintaining and updating test scripts easier as your application evolves.
Integrate with CI/CD: Embed automated E2E tests into your continuous integration and deployment pipelines. This ensures tests run with every code change, catching issues early and improving release quality.
Maintain Test Data Consistency: Use version-controlled, reliable test data to ensure repeatable and trustworthy test results across different runs and environments.
Document and Review: Keep your test cases and scripts well-documented. Regularly review and refactor them to avoid redundant or flaky tests that can slow down your automation pipeline.
By gradually introducing automation—beginning with the most repetitive or business-critical flows—you’ll free your team from repetitive manual testing and boost overall software quality. Automated E2E tests act as a safety net, validating that new features or changes haven’t compromised user experience or system stability.
Best Practices for End-to-end Testing
End-to-end (E2E) testing is crucial for ensuring your software operates smoothly from the user's perspective. Here are some essential best practices for effective E2E testing:
User-Centric Approach: Always prioritize the user's perspective. Focus on testing real-world user journeys and the functionalities they use most often.
Define Scope: Determine the scope of your E2E testing based on critical features and user workflows. This ensures resources are used efficiently.
Testing Environment: Set up a dedicated testing environment that closely mirrors the production setup. This reduces unexpected issues during deployment.
Clear Test Cases: Write clear, concise, and easy-to-understand test cases. Use descriptive names and steps to facilitate updates and collaboration.
Automation: Automate repetitive and time-consuming test cases using a suitable E2E testing framework. This frees up time for exploratory testing. Learn more about API automation testing here.
Monitor and Report: Monitor test execution, record results, and generate detailed reports for future reference. This helps identify trends and evaluate test effectiveness.
Security Integration: Incorporate security considerations into your E2E testing strategy. Simulate potential attacks and identify vulnerabilities before deployment.
Continuous Improvement: Each testing cycle provides valuable insights. Analyse results, pinpoint areas for improvement, and adjust your E2E testing strategy for better coverage and efficiency.
E2E testing is an ongoing process. By following these best practices and continuously refining your approach, you can ensure your software delivers a seamless user experience from start to finish. With Qodex.ai, you can enhance your E2E testing process, leveraging its powerful tools to streamline testing, automate tasks, and achieve greater accuracy and efficiency.
Some Tools for E2E Testing:
Qodex.ai
Cypress
Puppeteer
Katalon Studio
TestComplete
And here's the best part: With Qodex.ai, you don't need to be a coding wizard to unleash the power of E2E Testing. Our low-code platform lets anyone, even non-technical folks, create and run E2E tests with ease. Think drag-and-drop, plain English instructions, and AI guidance – it's like having your own personal testing sidekick!
Ready to ditch the testing stress and embrace E2E testing awesomeness?
Start your free Qodex.ai trial today and unleash your inner testing superhero!
Conclusion
End-to-end (E2E) testing is crucial for ensuring your software meets user expectations and functions seamlessly in real-world scenarios. By focusing on user journeys, defining clear test scopes, setting up realistic environments, and leveraging automation with tools like Qodex.ai, you can enhance testing efficiency and accuracy. Continuous monitoring, security integration, and ongoing improvements are key to maintaining software reliability and performance. Embrace these best practices to deliver a flawless user experience and ensure your software meets business goals effectively.
Let's explore how you can establish a comprehensive test infrastructure with Qodex.ai.
With Qodex.ai, you have an AI co-pilot Software Test Engineer at your service. Our autonomous AI Agent assists software development teams in conducting end-to-end testing for both frontend and backend services. This support enables teams to accelerate their release cycles by up to 2 times while reducing their QA budget by one-third.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why should you choose Qodex.ai?
Qodex.ai simplifies and accelerates the API testing process by leveraging AI-powered tools and automation. Here's why it stands out:
- AI-Powered Automation
Achieve 100% API testing automation without writing a single line of code. Qodex.ai’s cutting-edge AI reduces manual effort, delivering unmatched efficiency and precision.
- User-Friendly Platform
Effortlessly import API collections from Postman, Swagger, or application logs and begin testing in minutes. No steep learning curves or technical expertise required.
- Customizable Test Scenarios
Whether you’re using AI-assisted test generation or creating test cases manually, Qodex.ai adapts to your needs. Build robust scenarios tailored to your project requirements.
- Real-Time Monitoring and Reporting
Gain instant insights into API health, test success rates, and performance metrics. Our integrated dashboards ensure you’re always in control, identifying and addressing issues early.
- Scalable Collaboration Tools
Designed for teams of all sizes, Qodex.ai offers test plans, suites, and documentation that foster seamless collaboration. Perfect for startups, enterprises, and microservices architecture.
- Cost and Time Efficiency
Save time and resources by eliminating manual testing overhead. With Qodex.ai’s automation, you can focus on innovation while cutting operational costs.
- Continuous Integration/Delivery (CI/CD) Compatibility
Easily integrate Qodex.ai into your CI/CD pipelines to ensure consistent, automated testing throughout your development lifecycle.
How can I validate an email address using Python regex?
You can use the following regex pattern to validate an email address: ^[a-zA-Z0-9._%+-]+@[a-zA-Z0-9.-]+\.[a-zA-Z]{2,}$
What is Go Regex Tester?
Go Regex Tester is a specialized tool for developers to test and debug regular expressions in the Go programming environment. It offers real-time evaluation of regex patterns, aiding in efficient pattern development and troubleshooting
Discover, Test, & Secure your APIs 10x Faster than before
Auto-discover every endpoint, generate functional & security tests (OWASP Top 10), auto-heal as code changes, and run in CI/CD - no code needed.
Related Blogs