Understanding API Authentication: A Complete Guide
Introduction
API Authentication is the process of verifying the identity of a client application or user before allowing access to an API's resources. It ensures that only authorized entities can interact with the API and helps maintain the security and integrity of the system. There are various methods of API authentication, including API keys, OAuth tokens, and username/password authentication, each with its approach to verifying identities and ensuring secure access.
The Benefits of API Authentication
API authentication offers several benefits:
Security: Authentication ensures that only authorized users or systems can access the API, protecting sensitive data and resources from unauthorized access.
Data Integrity: By verifying the identity of users or systems, authentication helps maintain the integrity of data exchanged through the API, reducing the risk of tampering or manipulation.
Access Control: Authentication mechanisms allow API providers to enforce access control policies, determining which users or systems have permission to access specific resources or perform certain actions.
Auditing and Logging: Authentication provides a mechanism for tracking and logging API usage, enabling API providers to monitor access patterns, detect suspicious activity, and generate audit trails for compliance purposes.
By correlating API audit logs with other security data—such as those gathered by third-party SIEM tools—teams can gain a more comprehensive view of their security posture. Regular monitoring of audit logs helps ensure that only authorized users are interacting with the API, and makes it easier to identify and investigate anomalies or potential security incidents.
It's not enough to simply have authentication in place—ongoing monitoring of logs that record API access is essential. By regularly reviewing these logs, you can quickly spot unusual behavior, such as a sudden spike in failed login attempts or access from unexpected locations. This proactive approach helps you catch potential threats early and maintain the integrity of your API.
In addition to robust logging, Qodex.ai empowers teams to strengthen their API authentication workflows with a suite of practical features:Flexible Authentication Mechanisms: Choose from a variety of supported authentication strategies, including OAuth 2.0, API keys, JWT bearer tokens, and AWS signature. Set these at the request, collection, or folder level for seamless management and consistent enforcement.
Proactive Security Alerts: Automated governance tools warn you of authentication issues—such as exposed credentials or missing schemes—complete with actionable suggestions for remediation.
Token Exposure Scanning: The platform continuously scans public workspaces, collections, and environments for exposed authentication tokens. With built-in support for tokens from popular providers like OpenAI, Notion, and Twilio (and customizable scanning for others), you can catch leaks before they become liabilities.
Automatic OAuth 2.0 Token Refresh: No more manual intervention—Qodex.ai can refresh your OAuth 2.0 access tokens automatically, ensuring uninterrupted access and reducing administrative overhead.
Seamless API Authentication Guidance: Step-by-step guidance streamlines authentication with well-known APIs, helping users get up and running quickly and securely.
Comprehensive Audit Log Access: Visual dashboards and API endpoints make it easy to correlate audit logs with your other security and monitoring tools, so you always have a clear picture of who’s accessing your APIs and when.
With these features, Qodex.ai not only secures your APIs but also provides the visibility and control needed to respond swiftly to any authentication-related risks.
Personalization: Authentication enables API providers to personalize user experiences by identifying individual users or systems and delivering tailored content or services based on their unique profiles or permissions.
Regulatory Compliance: Many industries and jurisdictions have regulations and standards that require secure access control and authentication mechanisms. Implementing API authentication helps organizations comply with these requirements.
Why HTTPS Matters for API Authentication
When implementing API authentication, using HTTPS is not just recommended—it's essential. Many authentication methods, such as HTTP basic authentication and API key-based authentication, rely on transmitting sensitive information like usernames, passwords, or keys with each request. Without proper encryption, these credentials can be intercepted by attackers lurking on the network, putting your data and systems at risk.
HTTPS encrypts the data exchanged between the client and server, creating a secure tunnel that shields authentication details from prying eyes. This means that even if someone manages to capture the network traffic, they won't be able to decipher the credentials or other confidential information being sent.
In short, HTTPS transforms insecure authentication mechanisms into secure ones by ensuring that all communication—including the exchange of sensitive credentials—remains private and tamper-proof. Always combine your preferred authentication method with HTTPS to safeguard your APIs and maintain robust security standards.
API Authentication vs. Authorization
API authentication verifies the identity of a user or API request, requiring submission of information for access, such as login credentials or identity documents.
API authorization determines the resources or services an API request can access, allowing or denying requests based on authorization levels.
API authentication ensures user identity verification, while authorization controls access to API calls or requests.
Both authentication and authorization are crucial for API security, enhancing user experience, and safeguarding sensitive data.

API Authentication Methods
API Keys: Clients include a unique API key in the request headers, which the API server verifies for authentication. You can generate test keys with our API Key Generator. Example: `X-API-Key: your-api-key`
OAuth (Open Authorization): Third-party applications obtain access tokens (e.g., via OAuth2 flows) and include them in request headers to authenticate with the API.
Example: `Authorization: Bearer <access_token>`Basic Authentication: Users provide their username and password encoded in base64 format in the request headers.
Example: `Authorization: Basic base64Encoded(username:password)`This is one of the most straightforward methods of API authentication. With basic authentication, the credentials are sent as a user/password pair in the header. While the credentials are base64-encoded, it's important to note that this is not encryption—just a simple encoding. As a result, basic authentication is considered insecure if used alone, since anyone with access to the network traffic can easily decode the credentials. To mitigate this risk, basic authentication should always be used over HTTPS to ensure the credentials are transmitted securely.
Bearer Tokens: Clients include a bearer token obtained after authentication in the request headers for subsequent API requests. Example: `Authorization: Bearer <bearer_token>`
JSON Web Tokens (JWT): Users receive a JWT after successful authentication, which is then included in request headers for authentication. Example: `Authorization: Bearer <JWT>`|
JWTs are compact, digitally signed tokens that provide a stateless mechanism for API authentication. When a user logs in, the API server generates a signed (and often encrypted) JWT containing the user's identity and other relevant claims. Rather than storing session data on the server, the client attaches this JWT to each subsequent request header. The server then deserializes and validates the token to confirm the user's authenticity. This approach enhances scalability since the server doesn’t need to maintain session state for each user.Token-based Authentication: Clients receive a token after authentication, which is then included in request headers for subsequent API requests. Try generating sample tokens with our Token Generator. Example: `Authorization: Token <token>`
Certificate-based Authentication:The API server validates the client's certificate to authenticate the request. Example: Clients present a digital certificate issued by a trusted Certificate Authority (CA) for authentication.
Why Rely on a Well-Established Authentication Framework?
Developing your own custom authentication system might sound enticing, but it’s a risky move. Industry-standard frameworks—like OAuth, OpenID Connect, and JWT—are the result of countless hours of rigorous development, real-world testing, and ongoing community scrutiny.
Here’s why leveraging these established frameworks is the smarter path:
Battle-Tested Security: These frameworks have been refined to handle a wide variety of attacks. Relying on them means benefiting from security measures developed and vetted by experts worldwide.
Reduced Vulnerabilities: Custom code is far more likely to contain mistakes or oversights that attackers can exploit. Trusted solutions have already addressed many edge cases you might miss.
Faster Implementation: Avoid reinventing the wheel. Established frameworks come with comprehensive documentation and libraries that speed up integration, getting your API protected in less time.
Easier Maintenance: Security threats evolve. Community-backed frameworks are actively maintained and updated to address new vulnerabilities—keeping you safer without extra burden.
Simplified Compliance: Many regulatory standards point to established authentication mechanisms. Using a recognized protocol makes it easier for your organization to demonstrate compliance with industry regulations.
If security, reliability, and peace of mind are priorities, sticking with proven authentication protocols isn’t just best practice—it’s essential.
How Does API Authentication Work?
The dynamic of API authentication can differ, depending on the method you choose. The most common form of authentication is to send or receive an API key, which consists of a long series of letters or numbers.
This code of numbers calls programs from a different application; the key then recognises the code, its developer, the end-user, and the application where the API call is made from. When the client authenticates the API key, the server recognises their identity and lets them access data with ease.
Common Methods of API Authentication
API keys were made as a fix for early issues with HTTP basic authentication and other comparable systems. API keys have unique identifiers for users each time they try to authenticate. It’s perfectly suitable for applications that have several users seeking access.
A uniquely generated code or token is allocated to each first-time user to signify that the user is known. If they want to log in again, they use that code for verification.
OAuth with OpenID
This method of API authentication isn’t solely for authentication in its default state. It’s a combination of both authorization and authentication.
OAuth with Open ID provides authorization services to decide which users have access to various corporate information. When this is used solely for authentication, it’s called pseudo-authentication simply because it is not designed for that purpose.
When you combine OAuth and OpenID, it offers stronger authentication and authorization. Implementing both commands confirms that users and devices are using a third-party authentication process. The combination of OAuth and OpenID is one of the most reliable authentication/authorization options available on the market today.
How OAuth Works
OAuth is a token-based authentication mechanism that enables a user to grant third-party access to their account without having to share their login credentials. OAuth 2.0, which provides greater flexibility and scalability than OAuth 1.0, has become the gold standard for API authentication, allowing users to authorize apps to interact with their data securely. This approach is widely supported and enables extensive API integrations without putting user data at risk.
Benefits of OAuth and OpenID
Security: Instead of sharing passwords, users grant access using secure tokens, which can be limited in scope and duration.
Scalability: OAuth 2.0 supports complex enterprise use cases and large-scale integrations.
User Experience: Users can leverage existing accounts from trusted providers, avoiding the hassle of creating new credentials for every service.
Granular Access: Permissions can be fine-tuned to allow only the necessary level of access to data.
How to Select the Right API Authentication Method
When selecting the authentication method that is best for a particular API, it comes down to the level of security that is required to validate clients versus the ease of implementation and maintenance. HTTP Basic Authentication is easy to implement, but is also more vulnerable to account compromise since the password is not encrypted.
OAuth Authentication offers security, scalability, and the best user experience. However, it’s more work for developers and API providers to implement and maintain. Realistically, all the user needs to do is click on a button, but the real benefit is that the user can utilize an existing account and the app developers can leverage an existing authentication mechanism, which is less work than creating one on their own.
Another tool that complements OAuth is OpenID. This works as an identity layer you can deploy on top of the protocol so the API can verify a clients identity and profile via authentication performed by the authorization server.
This combination of OAuth and OpenID allows you to benefit from a stronger security posture. It contains a system that natively supports strong authorization in addition to embedded authentication methods, which decreases the cost of implementation over the long run.
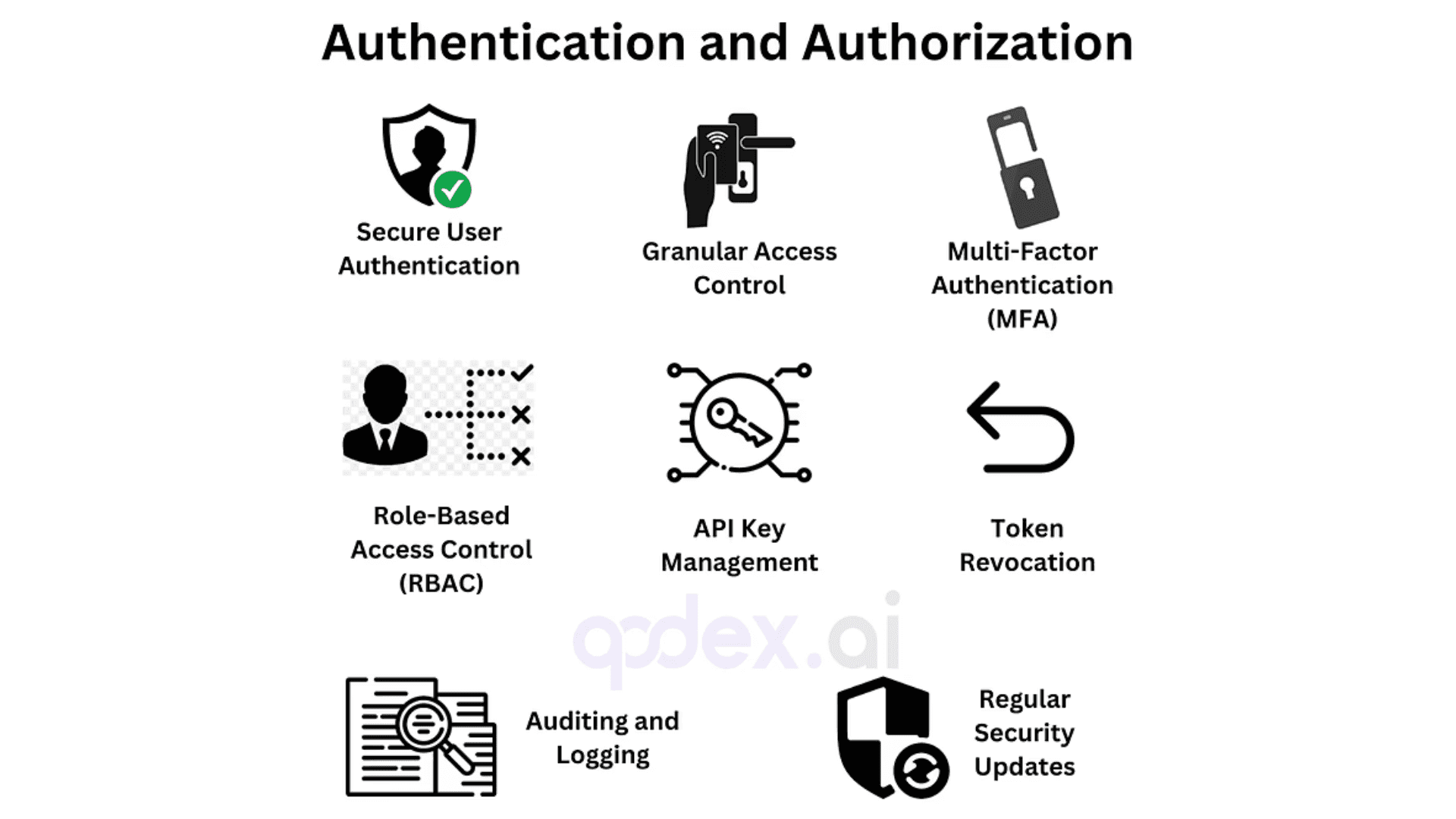
Authentication and Authorization with Qodex.ai
Secure User Authentication:
Qodex.ai ensures secure user authentication by implementing robust methods such as OAuth and JWT, verifying user identity before granting access. Always opt for well-established authentication frameworks rather than building your own from scratch—protocols like OAuth, OpenID Connect, and JWT have been thoroughly vetted for security and reliability.Granular Access Control:
Qodex.ai provides fine-grained access control, allowing administrators to define who can access specific API endpoints, ensuring that only authorized users have access to sensitive data. Choosing the appropriate authentication method is essential—consider your application's needs and the sensitivity of your data when selecting between options like OAuth, API keys, or HTTP basic authentication.Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA):
Enhance security with MFA, requiring users to provide two or more verification factors, reducing the risk of unauthorized access. Two-factor authentication (2FA) significantly increases security by making it more difficult for attackers to gain access, even if a password is compromised.
Implementing two-factor authentication (2FA)—which typically asks users for something they know (like a password) and something they have (such as a one-time token or authentication app)—adds a crucial extra layer of defense. By combining these authentication methods, it becomes significantly more difficult for attackers to compromise access, even if one factor is exposed.Role-Based Access Control (RBAC):
With Qodex.ai, assign roles to users and manage permissions based on these roles, ensuring that users only have the necessary access to perform their tasks.API Key Management:
Qodex.ai simplifies the management of API keys, providing secure ways to generate, distribute, and revoke keys as needed. When using API keys or similar mechanisms, always ensure that all communications occur over HTTPS to keep credentials and data encrypted and protected from interception.Token Revocation:
Instantly revoke access tokens if they are compromised, ensuring unauthorized users cannot access the system.Auditing and Logging:
Qodex.ai keeps detailed logs of authentication and authorization events, making it easy to track and respond to suspicious activities. Monitoring API access through comprehensive logs helps detect unusual activity, such as multiple failed login attempts or logins from unfamiliar locations.Regular Security Updates:
Stay protected with regular security updates from Qodex.ai, addressing new vulnerabilities and enhancing authentication and authorization protocols.
Additional Best Practices:Always use HTTPS: Never expose authentication credentials—such as API keys or tokens—over unencrypted channels. HTTPS is essential to prevent eavesdropping and ensure that sensitive data stays secure.
Monitor and Respond: Regularly review access logs and set up alerts for suspicious behavior to catch issues early.
Avoid Outdated Methods: Steer clear of outdated and vulnerable authentication methods like HTTP basic authentication in production environments.
By following these best practices and leveraging Qodex.ai’s robust authentication and authorization features, you can safeguard your APIs and protect sensitive data from emerging threats.
Additional Security Features for Robust API Protection
Support for Multiple Authentication Mechanisms:
Leverage a comprehensive suite of authentication options—such as OAuth 2.0, API keys, JWT bearer tokens, and even AWS signature verification—flexibly applied at the request, collection, or folder level to streamline management and ensure consistency.Security Alerts and Guidance:
Benefit from proactive security alerts that flag authentication issues, such as missing or misconfigured schemes, exposed authentication data, or weak credentials. Clear, actionable guidance helps administrators resolve risks quickly and confidently.Automatic Detection of Exposed Tokens:
Qodex.ai automatically scans your public-facing API endpoints, collections, and environments for exposed authentication tokens—including those from popular services like OpenAI, Notion, and Twilio. Custom detection patterns can be added for proprietary or third-party tokens to further strengthen your security posture.Token Lifecycle Management:
Tokens, especially OAuth 2.0 access tokens, can be automatically refreshed before expiration. This eliminates the hassle of repeated manual authorizations and ensures ongoing secure access.Streamlined Authentication for Popular APIs:
Quickly connect with leading public APIs—such as OpenAI, Notion, and Twilio—through guided authentication workflows. These integrations reduce setup complexity and speed up your time to first successful API call.Comprehensive Audit Logging:
Monitor authentication and authorization events through unified audit logs. These can be accessed via dashboard or API, enabling integration with third-party security information and event management (SIEM) tools for advanced monitoring and correlation.
By combining these advanced authentication and authorization capabilities, Qodex.ai empowers teams to secure their APIs with confidence, minimize risks, and maintain compliance with modern security standards.
Getting Started
API authentication provides a secure way for users to access resources or services. By using API authentication methods, organizations can quickly verify user identities. You'll ensure that only authorized users have access to the resources you offer.
API authentication provides an invaluable layer of security for any organization. So get started with authentication to protect your users and ensure the safety of their data.
"Stay connected with us for the latest updates, insights, and exciting content! 🚀 Follow us on X and LinkedIn. Hit the 'Like' button, give us a 'Follow,' and don't forget to 'Share' to spread the knowledge and inspiration.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why should you choose Qodex.ai?
Qodex.ai simplifies and accelerates the API testing process by leveraging AI-powered tools and automation. Here's why it stands out:
- AI-Powered Automation
Achieve 100% API testing automation without writing a single line of code. Qodex.ai’s cutting-edge AI reduces manual effort, delivering unmatched efficiency and precision.
- User-Friendly Platform
Effortlessly import API collections from Postman, Swagger, or application logs and begin testing in minutes. No steep learning curves or technical expertise required.
- Customizable Test Scenarios
Whether you’re using AI-assisted test generation or creating test cases manually, Qodex.ai adapts to your needs. Build robust scenarios tailored to your project requirements.
- Real-Time Monitoring and Reporting
Gain instant insights into API health, test success rates, and performance metrics. Our integrated dashboards ensure you’re always in control, identifying and addressing issues early.
- Scalable Collaboration Tools
Designed for teams of all sizes, Qodex.ai offers test plans, suites, and documentation that foster seamless collaboration. Perfect for startups, enterprises, and microservices architecture.
- Cost and Time Efficiency
Save time and resources by eliminating manual testing overhead. With Qodex.ai’s automation, you can focus on innovation while cutting operational costs.
- Continuous Integration/Delivery (CI/CD) Compatibility
Easily integrate Qodex.ai into your CI/CD pipelines to ensure consistent, automated testing throughout your development lifecycle.
How can I validate an email address using Python regex?
You can use the following regex pattern to validate an email address: ^[a-zA-Z0-9._%+-]+@[a-zA-Z0-9.-]+\.[a-zA-Z]{2,}$
What is Go Regex Tester?
Go Regex Tester is a specialized tool for developers to test and debug regular expressions in the Go programming environment. It offers real-time evaluation of regex patterns, aiding in efficient pattern development and troubleshooting
Discover, Test, & Secure your APIs 10x Faster than before
Auto-discover every endpoint, generate functional & security tests (OWASP Top 10), auto-heal as code changes, and run in CI/CD - no code needed.
Related Blogs





